Your Ad Here
In addition to being used as food additives, monoglycerides also are employed as polymer additives. Therefore, the need for more efficient methods of monoglyceride preparation is obvious. Their consumption in Europe exceeds 20,000 tons per annum.
The 2009-2014 Outlook for Monoglycerides in the United States
Monoglycerides of a purity lower than 90% are derived either from the catalytic transesterification of glycerol with triacytglycerols or from the direct esterification of free fatty acids with glycerol.
For the industrial preparation of monoglycerides of purity higher than 90%, synthesized monoglycerides undergo molecular distillation, a process which increases their manufacturing cost.
Need to know more? Search for related books at Google Books.
Submit Your Site to Best of the Web!
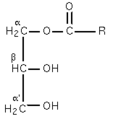
A monoglyceride, more correctly known as a monoacylglycerol, is a glyceride consisting of one fatty acid chain covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through an ester linkage.
The 2009-2014 Outlook for Monoglycerides in the United States
Monoglycerides of a purity lower than 90% are derived either from the catalytic transesterification of glycerol with triacytglycerols or from the direct esterification of free fatty acids with glycerol.
For the industrial preparation of monoglycerides of purity higher than 90%, synthesized monoglycerides undergo molecular distillation, a process which increases their manufacturing cost.
Need to know more? Search for related books at Google Books.
No comments:
Post a Comment